The first question is, what are grains? Well, grains are small, hard, dry seeds of cereal grass such as wheat, rye, millet, oats, barley, rice, and corn.
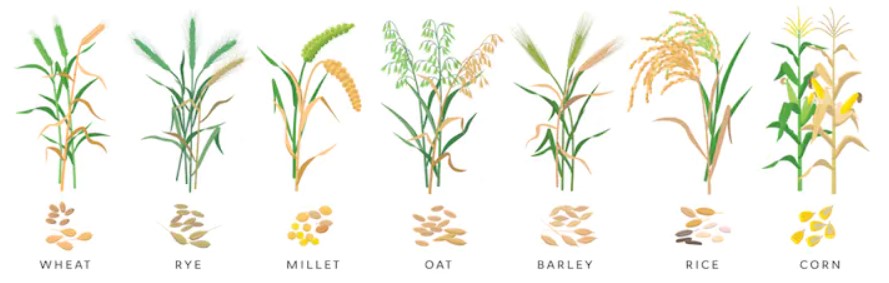
In this article we will take a look at a list of grains and types of grains.
Grains list and types of grains with pictures
Some consider pulses and oil seeds among grains bu we will focus on cereal grains here. Cereal grains contain a high amount of starch that provides dietary energy and all cereal crops are members of the grass family. We can classify grains into two main categories: Genuine cereal grains and pseudo cereal grains.
Genuine cereal grains
Barley (Hordeum vulgare)

Barley has been used as animal fodder, as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various health foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread of various cultures.
Nutrients in barley: Barley contains copper, magnesium, selenium, and zinc, which help to neutralize free radicals while boosting cell renewal, collagen synthesis, and overall elasticity. Barley is known for its antioxidant and inflammatory benefits to help inhibit environmental damage and reduce the appearance of skin aging.
Corn (maize, Zea mays)
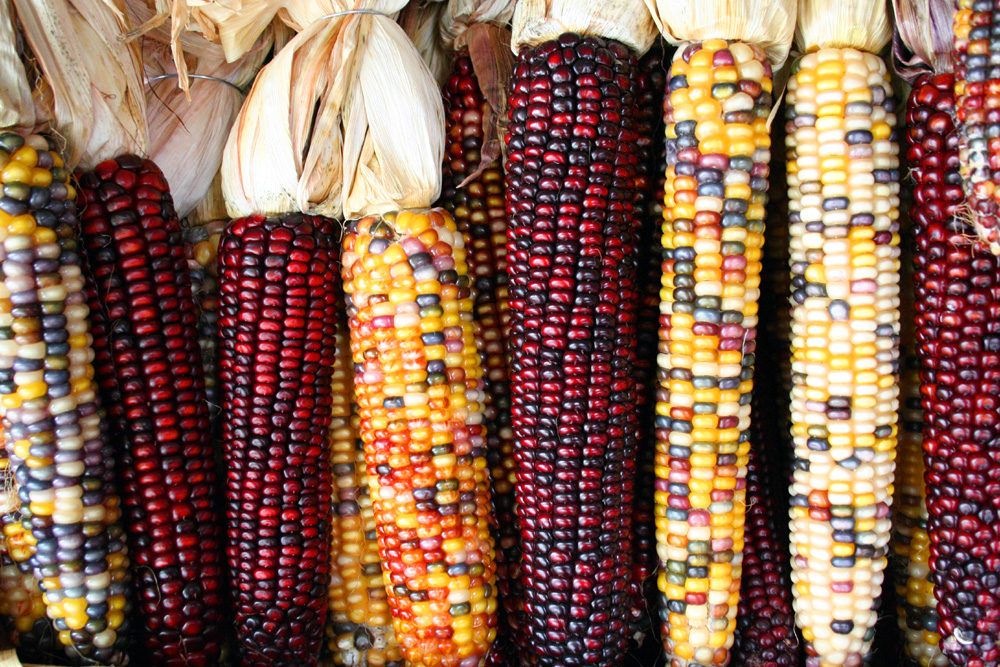

Maize, also known as corn, is a cereal grain which is also used for corn ethanol, animal feed and other maize products, such as corn starch and corn syrup. The six major types of maize are dent corn, flint corn, pod corn, popcorn, flour corn, and sweet corn.
Genetically modified maize made up 85% of the maize planted in the United States in 2009.
Corn oil is a common ingredient in face oils and moisturizers to help prevent skin dryness and boost antioxidant activity to keep skin cells hydrated.
Nutrients in corn: Corn is an antioxidant-rich grain containing vitamins B, C, and tocopherol (vitamin E), which helps relieve skin irritations, eczema, and blemish-prone skin. Corn oil is rich in magnesium and potassium.
Fonio (Digitaria)

Fonio is the term for two cultivated grasses in the genus Digitaria that are notable crops in parts of West Africa. They are millets with small grains. Fonio is a nutritious food with a favorable taste.
Millets

Millets are a group of highly variable small-seeded grasses. The different species of millets are not necessarily closely related. All are members of the family Poaceae (the grasses) but can belong to different tribes or even subfamilies. Millets may have been consumed by humans for about 7,000 years.
Finger millet (Eleusine coracana)

Eleusine coracana, or finger millet, is an annual herbaceous plant widely grown as a cereal crop in the arid and semiarid areas in Africa and Asia. It is commonly called kodo in Nepal where 877 accessions have been maintained by National Plant Genetic Resource Centre, Khumaltar, Nepal. It is a tetraploid and self-pollinating species.
Foxtail millet (Setaria italica)
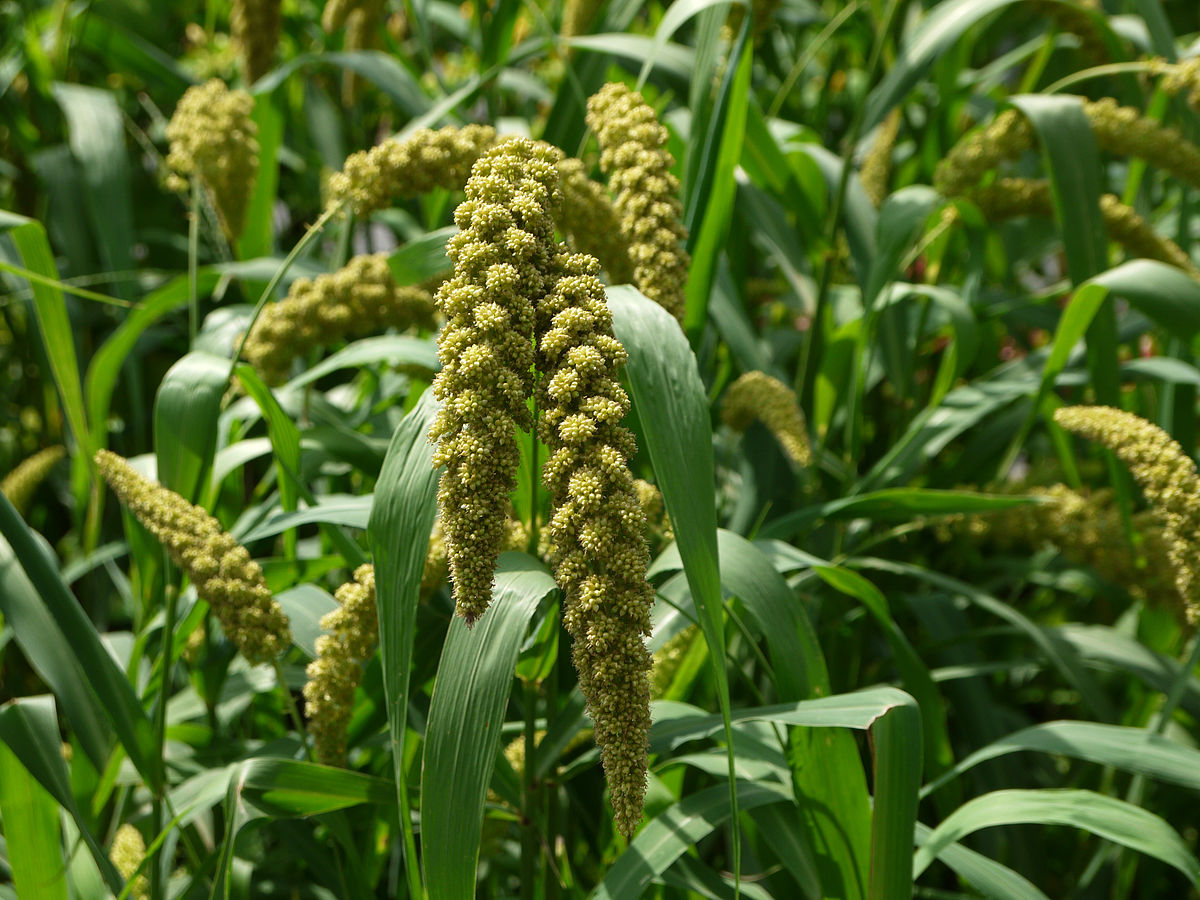

Foxtail millet (Setaria italica), is an annual grass grown for human food.
Other names for the species include dwarf setaria, foxtail bristle-grass, giant setaria, green foxtail, Italian millet, German millet, and Hungarian millet.
Japanese millet (Echinochloa esculenta)

Echinochloa esculenta is referred to by the common names Japanese barnyard millet or Japanese millet, both as a food and for animal fodder.
Oats (Avena sativa)

The oat is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human consumption as oatmeal and oat milk. Oats are associated with lower blood cholesterol when consumed regularly.
In cosmetics, oats are known for soothing, softening, and moisturizing sensitive skin. Derived from oats, beta glucan promotes hydration while maintaining the integrity of the skin’s moisture barrier. Oat extract is found in exfoliants, masks, creams, and serums to help calm skin irritation, stimulate collagen production, and promote healing.
Nutrients in oats: Oats are a source of anti-inflammatory minerals such as copper, magnesium, and selenium.
Rice (Oryza sativa)

Rice is the seed of the grass species Oryza glaberrima (African rice) or Oryza sativa (Asian rice). As a cereal grain, it is the most widely consumed staple food. There are many varieties of rice and culinary preferences tend to vary regionally. Click here for different types of rice to use in different recipes.
Nutrients in rice: Minerals in rice include magnesium, manganese, selenium, copper, and phosphorus, which provide anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits for stressed and photo-damaged skin. Rice water can be used in cleansers, toners, and exfoliants to help minimize pore size, smooth rough texture, and brighten skin tone.
Rye (Secale cereale)
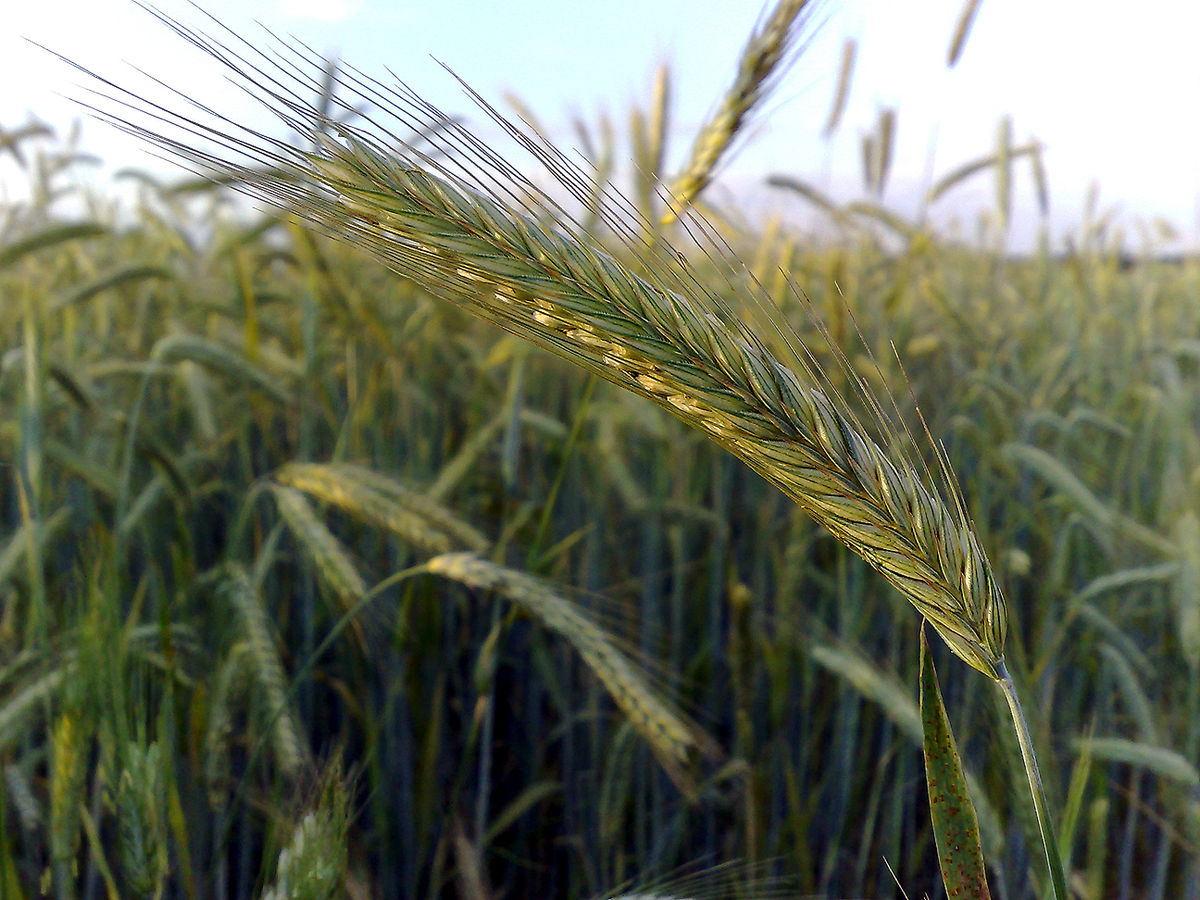

Rye is a grass grown extensively as a grain. Rye grain is used for flour, bread, beer, crispbread, some whiskeys, some vodkas, and animal fodder. It can also be eaten whole, either as boiled rye berries or by being rolled, similar to rolled oats.
Rye is a cereal grain and should not be confused with ryegrass, which is used for lawns, pasture, and hay for livestock.
Nutrients in rye: Rye has high levels of ferulic acid, magnesium, manganese, and vitamin E, which help improve cell function and blood flow and maintain moisture levels.
Spelt (Triticum spelta)

Spelt, also known as dinkel wheat or hulled wheat, is a species of wheat that has been cultivated since approximately 5000 BC.
Spelt was an important staple food in parts of Europe from the Bronze Age to medieval times. Now it survives as a relict crop in Central Europe and northern Spain, and has also found a new market as a health food.
Wheat (Triticum aestivum)
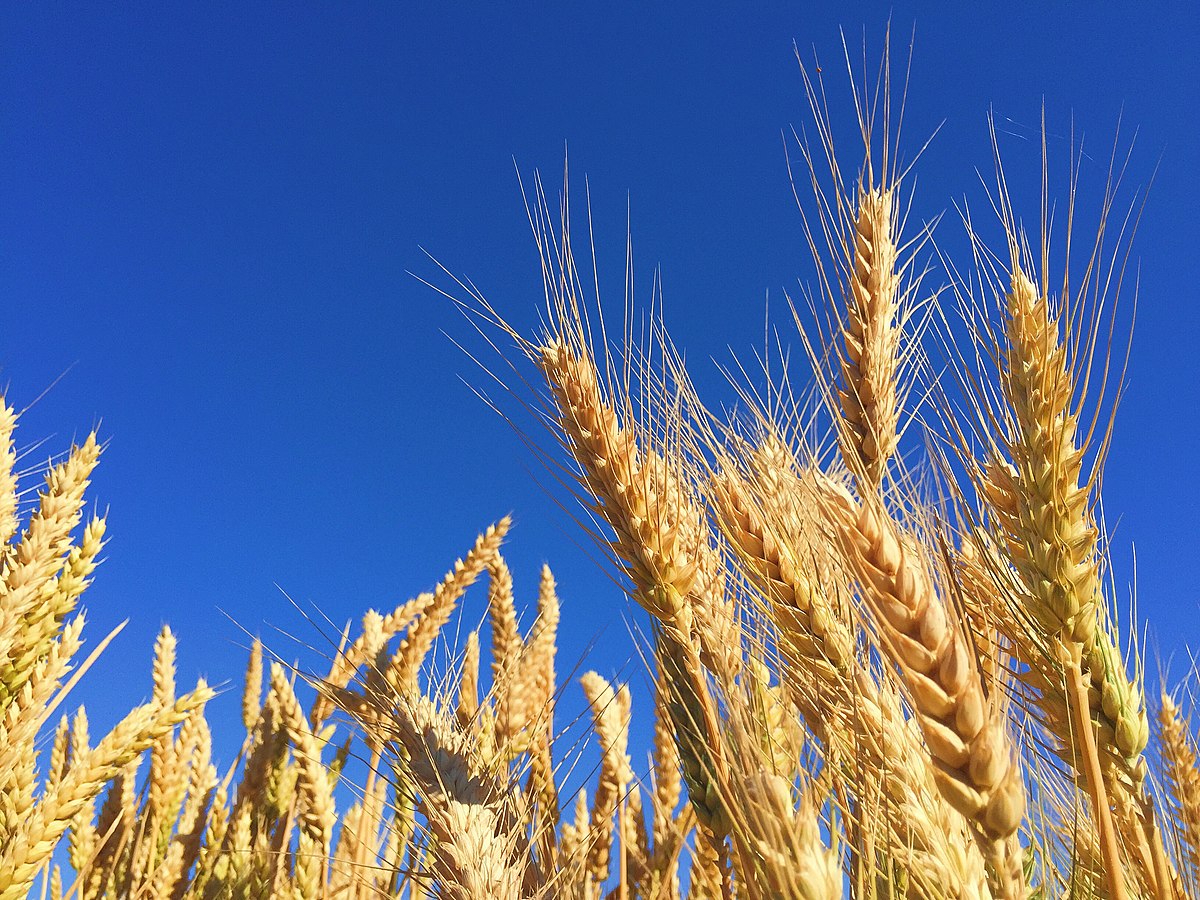

Wheat is an important source of carbohydrates. Globally, it is the leading source of vegetable protein in human food, having a protein content of about 13%, which is relatively high compared to other major cereals but relatively low in protein quality for supplying essential amino acids. When eaten as the whole grain, wheat is a source of multiple nutrients and dietary fiber.
In a small part of the general population, gluten – the major part of wheat protein – can trigger coeliac disease, noncoeliac gluten sensitivity, gluten ataxia, and dermatitis herpetiformis.
Wheat also is used to produce bulgur (also known as burghul), a cereal which has been partially processed, so cooks quickly.
Pseudo cereal grains
Buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum)
Buckwheat is a plant cultivated for its grain-like seeds. Despite the name, buckwheat is not related to wheat, as it is not a grass. Instead, buckwheat is related to sorrel, knotweed, and rhubarb. Buckwheat is referred to as a pseudocereal because its seeds’ culinary use is the same as cereals’, owing to their composition of complex carbohydrates.
Chia (Salvia hispanica)

Chia is a species of flowering plant in the mint family. It is considered a pseudocereal, cultivated for its edible, hydrophilic chia seed.
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa)
Quinoa is a flowering plant in the amaranth family. It’s seeds are rich in protein, dietary fiber, B vitamins, and dietary minerals in amounts greater than in many grains. Quinoa is not a grass, but rather a pseudocereal botanically related to spinach and amaranth. Quinoa seed extract is used in cosmetics because it enhances moisture retention and helps to firm skin.
Nutrients in quinoa: Quinoa is rich in minerals like copper, iron, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc, which help prevent environmental damage and support collagen production.


