In the world of plastic manufacturing, the terms “Thermoforming Mould” and “Thermoforming Mold” play a crucial role in producing high-quality products used across various industries. These terms refer to the custom-designed tools or templates used in the thermoforming process, a widely adopted method of shaping plastic materials. Understanding the basics of thermoforming moulds and how they work is essential for any company or individual involved in plastic production.
In the world of plastic manufacturing, the terms “Thermoforming Mould” and “Thermoforming Mold” play a crucial role in producing high-quality products used across various industries. These terms refer to the custom-designed tools or templates used in the thermoforming process, a widely adopted method of shaping plastic materials. Understanding the basics of thermoforming moulds and how they work is essential for any company or individual involved in plastic production.
What is Thermoforming?
The process itself can be broken down into several steps:
Heating: The plastic sheet is heated until it reaches a temperature where it becomes soft and flexible.
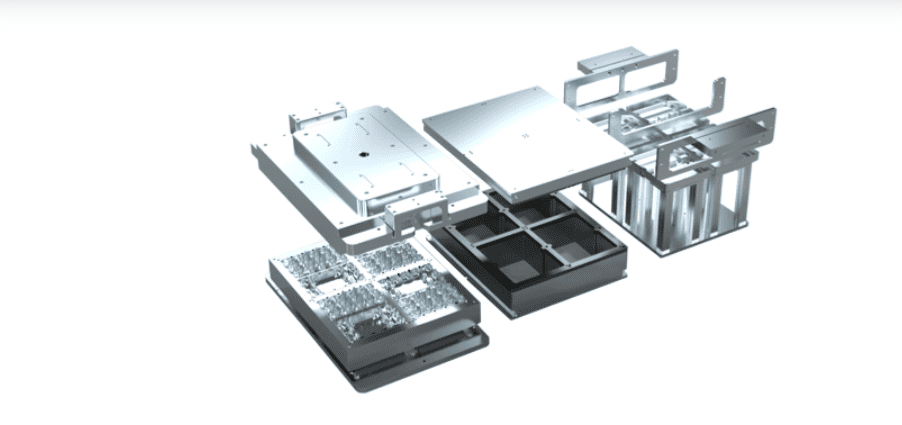
Moulding: The heated sheet is then draped over or into a pre-designed thermoforming mould.
Cooling: Once the plastic takes the shape of the mould, it is cooled to solidify the material.
Trimming: The excess plastic is trimmed to finish the product.
The Role of Thermoforming Moulds and Molds
Types of Thermoforming Moulds
Male Molds: In this type, the mould has a protruding shape that the heated plastic sheet is draped over. This type is often used for creating containers, trays, and other deep-drawn products.
Female Molds: A female mould has a recessed shape that the plastic sheet is pulled into, often used for creating hollow objects such as cups, bowls, and packaging.
Combination Molds: These are hybrid moulds that combine both male and female features, providing more flexibility in the design of the final product.
Each type of mould is carefully crafted to meet the specifications of the product being produced, with various materials and coatings available to suit different requirements.
Materials Used for Thermoforming Moulds
Aluminum: Aluminum is one of the most popular choices for thermoforming moulds due to its lightweight, durability, and excellent heat conductivity. Aluminum molds can be machined with precision and are cost-effective for both short and long production runs.
Steel: For high-volume production or when a higher degree of durability is required, steel is often used for thermoforming moulds. Steel moulds are more robust and can withstand higher temperatures and pressure, although they come with a higher initial cost.
Copper: Copper is sometimes used for thermoforming molds that require quick heat dissipation, especially when working with materials that are sensitive to heat.
Importance of Thermoforming Mould Design
The design of the thermoforming mould plays a critical role in the final product’s quality and functionality. A well-designed mould ensures that the plastic sheet is uniformly heated and shaped, which leads to precise, defect-free products. Key considerations in the design process include:
Heat Distribution: Proper heat distribution within the mould ensures that the plastic sheet is uniformly heated, leading to consistent results in the final product.
Ventilation: Adequate venting is crucial to prevent air pockets and ensure smooth forming. Without proper ventilation, defects such as bubbles and warping can occur.
Ease of Removal: The design of the mould should allow for easy removal of the finished product, ensuring that it does not become stuck or damaged during the process.
Thermoforming moulds must be carefully engineered to ensure efficiency and quality during production. With advancements in 3D modeling and simulation software, manufacturers can now design thermoforming moulds with a high level of precision, reducing the risk of defects and improving the overall production process.
Applications of Thermoforming Moulds
Thermoforming is used across many industries, and the moulds designed for the process can create products in various sectors. Some of the most common applications include:
Packaging: Thermoformed plastic packaging is widely used for food containers, blister packs, and other consumer goods. The moulds used to create these products are often designed for high-volume production and precise shapes.
Automotive: In the automotive industry, thermoforming is used to create parts such as dashboards, trim, and interior panels. Moulds in this sector often need to accommodate more complex designs and higher material strength.
Medical Devices: Medical packaging and trays often require thermoforming to ensure the safety and sterility of the items. Custom moulds are created to meet the strict standards of the medical field.
Consumer Goods: From toys to electronic housings, thermoforming is used to create a wide variety of consumer products, each with its unique design requirements.

Leave a Reply